
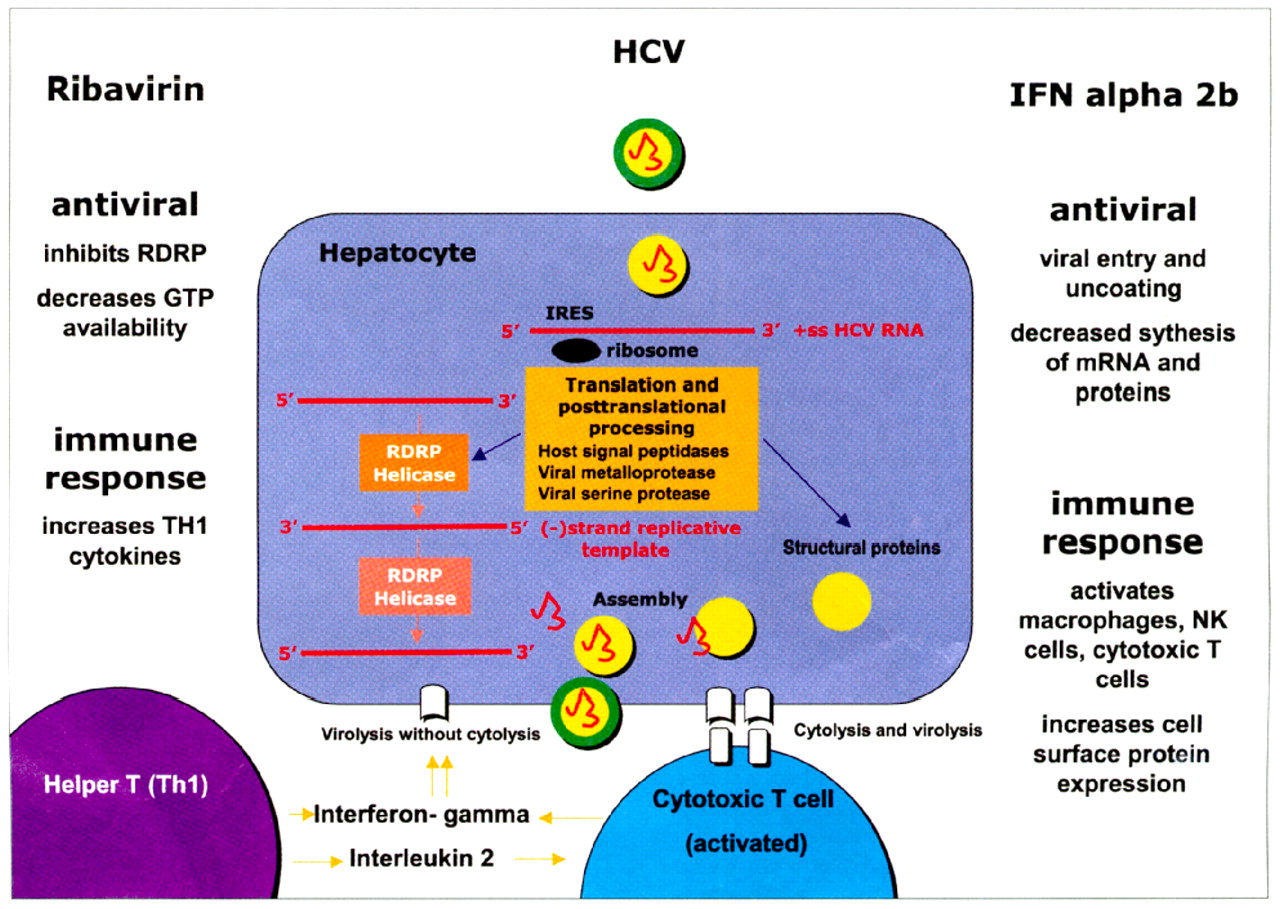
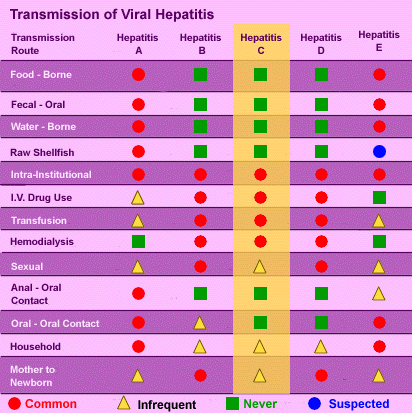
The following documents provide guidance on how to prepare for, detect, investigate and respond to an hepatitis C or HIV outbreak among people who inject drugs. The opioid misuse epidemic has substantially increased the transmission risk of blood-borne viruses, including hepatitis C virus and HIV, through injection drug use. Although hepatitis C is not generally considered to be a sexually transmissible infection in Australia, you may wish to consider safe sex practices (using a. In Egypt, for example, roughly 1015 percent of people between ages 15 and 59 are. The hepatitis C virus is a bloodborne virus and most infection occur through exposure to blood from unsafe injection practices, unsafe health care, unscreened blood transfusions, injection drug use and sexual practices that lead to exposure to blood. The burden of HCV infection varies depending on country and population. HCV is transmitted primarily through: Sharing contaminated needles. Risk factors to date are injection drug use, blood transfusions, accidental needlestick injuries. transmission, although this route is less efficient. About 71 million people worldwide have chronic HCV infection, making hepatitis C a major source of chronic liver disease. Transmission of HCV occurs via direct blood-to-blood contact. In recent years, there has been an emerging HCV epidemic among young PWIDs, particularly in rural and suburban settings. hepatitis C, infectious disease of the liver, the causative agent of which is known as hepatitis C virus (HCV). The hepatitis C virus is a bloodborne virus and most infection occur through exposure to blood from unsafe. The virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging in severity from a mild illness to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and cancer. About 10 of people with HCV infection have no recognized. Hepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus. HCV can be transmitted to the infant in utero or during the peripartum period PHE, 2018a PHE, 2018b. The highest reported incidence of acute hepatitis C in the United States is now among persons aged 20–29 years. Vertical transmission of HCV from mother to baby generally occurs at a low rate (48), but higher rates (10.825) are seen if the mother is co-infected with HIV WHO, 2018.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
